In this article the topics we discuss are,
- What is sensitive data?
- Tracking the sensitive data audit access | Know about the feature 21B on oracle HCM cloud business
- Steps for sensitive data access auditing
So, what is sensitive data?
Sensitive data is the information that is considered to be more confidential, and kept more secure, protecting from outsiders unless they have permission to access it.
Access to any sensitive data must be finite via adequate information security practices, which are designed to control the leakage of data and breaches.
Know About Oracle HCM Cloud Feature 21B
A Feature that was released in 21B, but not much explored, is that one can track the viewing of sensitive data Audit in the HCM Responsive pages.
The IT team can track the IP address of the user, device (Mobile/Laptop), Audit Date, Audit Time, Browser, Operating System used Username, Page Title which was viewed, etc.
Below is the list of sensitive data that can be audited.
- National Identifier Number
- Passport Number
- Driver License Number
- Personal Home Address
- Personal Email Address
- Personal Telephone Number
- Account Number
- Citizenship Number
- Visa Number, Residency Number, and Work Permit
Roles/privileges required to access this functionality:
Assign the PER_VIEW_SENSITIVE_DATA_ACCESS_AUDIT_PRIV privilege to the user and this privilege is granted to the Predefined IT Auditor role.
Steps to Enable Sensitive Data Access Audit
Default profile value to be set as “Y”. This will enable the “Sensitive Data Access Audit” option. To enable or check the default profile value, these are the steps to be followed:
Step 1: In the Setup and Maintenance work area, search for and click the Manage Administrator Profile Values task.
Step 2: On the Manage Administrator Profile Values page, Search for the ORA_HCM_SENSITIVE_DATA_VIEW_AUDIT_ENABLED profile option code
Step 3: In the Profile Values area, Select Profile level to Site and enter Y in the Profile Value field.
Step 4: Click Save and Close.
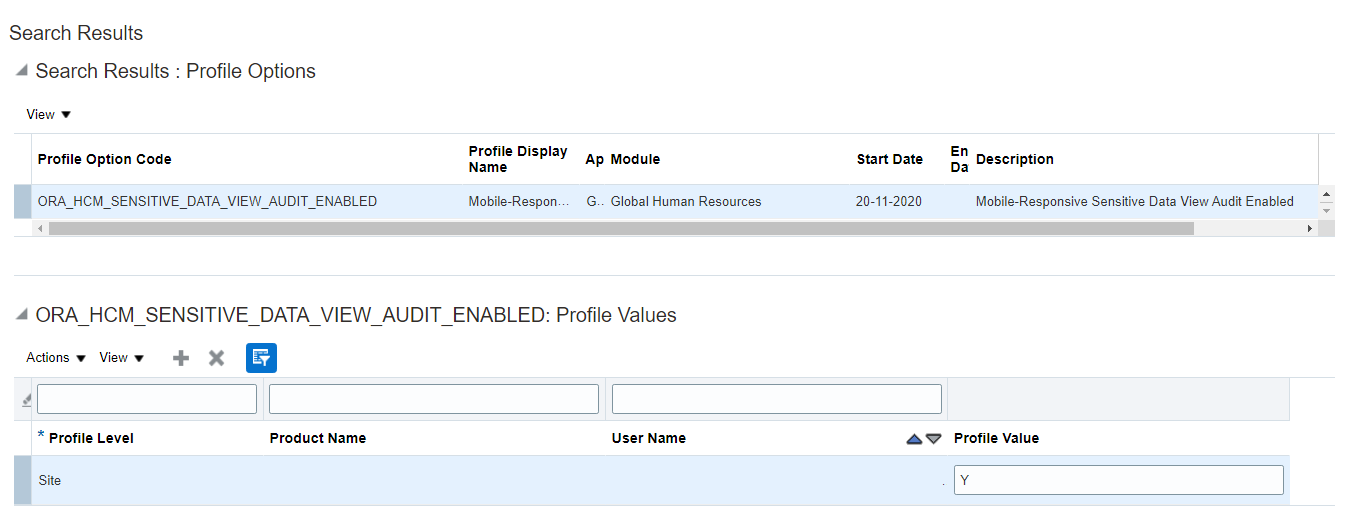
Fig 1: Manage Administrator Profile Values
IT Auditor can view the new responsive page under My client group à Sensitive Data Access Audit (Quick Actions)
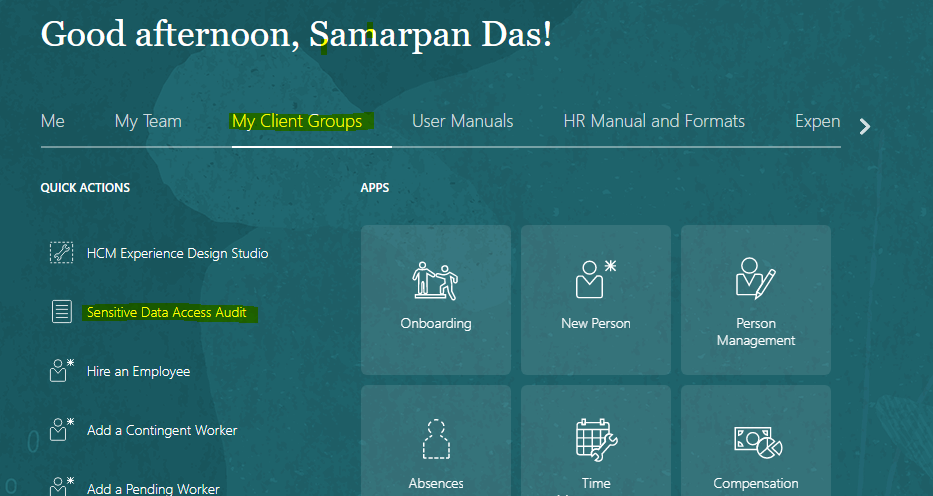 Fig 2: Home Page
Fig 2: Home Page
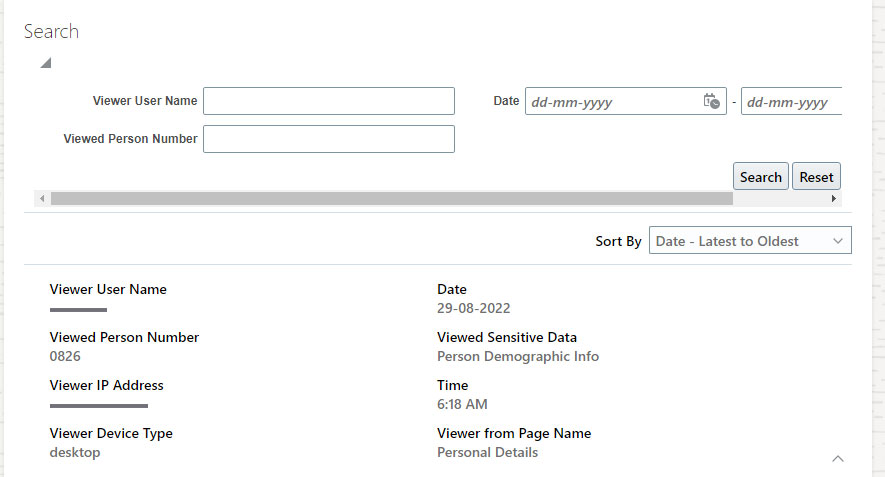
Fig 3: Oracle HCM Sensitive Data Access Audit
Subject Area to get this information:
Users can get this information from the “Workforce Management – Sensitive Data Access Audit Real Time” subject area. Enables us to track and report the details about the sensitive data that is accessed from the Oracle HCM Cloud page.
Key information that you can report on
- Viewed Person Details – The person’s details data has been accessed
- Viewer Person Details – The person’s details who has accessed sensitive data
- Viewed Page Name
- Viewed Sensitive Data
- Viewed Date and time
- Viewer IP address, Browser, Operating system, etc.
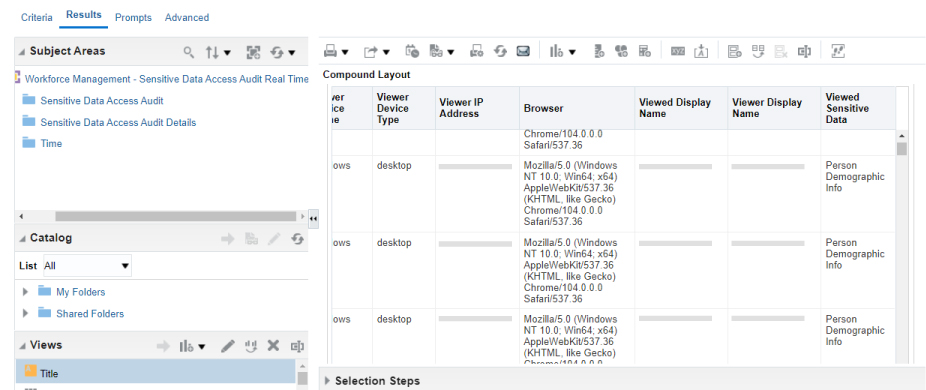
Fig 4: OTBI Report
Back-end Table to get this information:
A report can be prepared and scheduled by querying the back-end table to get this information.
PER_SENSITIVE_DATA_AUDIT is the table that stores the sensitive data audit information.
Sample queries: Query to get records by logged-in user name
select * from per_sensitive_data_audit where viewer_user_name = ” order by creation_date desc
Query to get records by logging in user name & IP address of the machine
select * from per_sensitive_data_audit where viewer_user_name = ” and ip_address=” order by creation_date desc
Limitations:
- It is in read-only mode.
- Need to add Roles, and privileges and include a profile to avail of this service
- Limited to only specific Attributes as mentioned Above
- The audit report is available after the user has signed out /the session timed out/ clicked more than 20 times.
Business Benefits:
- IT auditors can Easily track the viewing of sensitive data.
- New Responsive User Interface.
- IT auditors can track the IP Address, Browser, and Operating system as well
Sensitive data access auditing
The sensitive data access auditing offers an expensive and difficult wall to regulatory compliance with industry regulations, government regulations, and privacy acts. The requirements for any particular audit will vary based on the regulations, but people will consider data access auditing as the key control which assists to secure the regulated data.
To encounter the required compliance, the data audit trail must represent the below points.
- Make sure to audit all the sensitive data access
- Offer the most detailed event information audit
- Build and establish the user accountability
- Assure the trail audit integrity
- Validate whether all the systems in scope are audited in the right way
- Customizable compliance reports, alertness, and analytical tools
1. Make sure to audit all the sensitive data access
An audit key must deliver visibility into all the data access events. So, it has to audit
- All the different types of access
- Each and every user
- All the data systems holding regulated data
2. Offer the most detailed event information audit
If you want to reconstruct the data access events more effectively, make an audit trail with a clear picture by answering – Who, Where, What, How, and When. Grabbing both the system response attributes and the raw access query is an essential element for more sufficient forensic investigation and incident response.
3. Build and establish the user accountability
The audit trail that you are performing must associate with each data access event to a particular user. It is hard for most of the applications, as it uses connection pooling, which has the capability to mask the actual identity of the end user.
4. Assure the trail audit integrity
The performing data audit trail should be tamper-proof. Tamper-proof is nothing but, that the audited users cannot alter the audit trail content. Here splitting the duties is more significant to protect the privileged users from manipulating their claims to conceal the irregular movements.
5. Validate whether all the systems in scope are audited in the right way
As all we know, all the file servers and the databases holding the regulated and sensitive data must be audited. Automated discovery and classification abilities allow the rapid identification of regulated systems and minimize compliance maintenance costs.
6. Customizable compliance reports, alertness, and analytical tools
For demonstrating compliance, audit reports are mandatory. The predefined reports will stay as a point to kickstart and assist address to respective audit needs for each regulation, while the customizability supports the unique business and technical requirements. The right audit tools and real-time alerts will allow for exhaustive forensic investigation and incident response.

